NASA-BRIEF-66-10038
- Version
- 75 Downloads
- 124.21 KB File Size
- 1 File Count
- August 19, 2017 Create Date
- August 19, 2017 Last Updated
Circuit Operates as Sine Function Generator
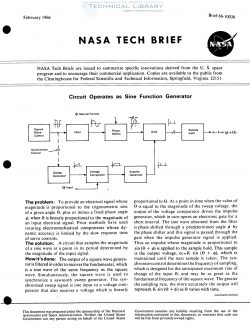
The problem: To provide an electrical signal whose
magnitude is proportional to the trigonometric sine
of a given angle 9, plus or minus a fixed phase angle
:15, when 9 is linearly proportional to the magnitude of
an input electrical signal. Prior methods have used
rotating electromechanical components whose dy-
namic accuracy is limited by the slow response time
of servo controls.
The solution l. A circuit that samples the magnitude
of a sine wave at a point in its period determined by
the magnitude of the input signal.
How it's done: The output of a square wave genera-
tor is filtered in order to recover the fundamental, which
is a sine wave of the same frequency as the square
wave. Simultaneously, the square wave is used to
synchronize a sawtooth sweep generator. The syn-
chronized sweep signal is one input to a voltage com-
parator that also receives a voltage which is linearly
proportional to 9. At a point in time when the value of
0 is equal to the magnitude of the sweep voltage.
The output of the voltage comparator drives the impulse
generator, which in turn opens an electronic gate for a
short interval. The sine wave obtained from the filter
is phase shifted through a predetermined angle (15 by
the phase shifter and this signal is passed through the
gate when the impulse generator signal is applied.
Thus an impulse whose magnitude is proportional to
sin (6 + ¢) is applied to the sample hold. This sample
is the output voltage, eo=K sin (6 + 4)), which is
maintained until the next sample is taken. The syn-
chronism control determines the frequency of sampling.
which is designed for the anticipated maximum rate of
change of the input 9, and may be as great as the
fundamental frequency of the square wave. The greater
the sampling rate. the more accurately the output will
represent K sin (6 + <15) as 9 varies with time.
| File | Action |
|---|---|
| NASA-BRIEF-66-10038 Circuit Operates as Sine Function Generator.pdf | Download |

Comment On This Post